Buddhism in India: Ancient Buddhism in India
Buddhism stands for 3 pillars:
1) Buddha: Its founder
2) Dhamma: His Teachings
3) Sangha: Order of buddhist monks and nuns.
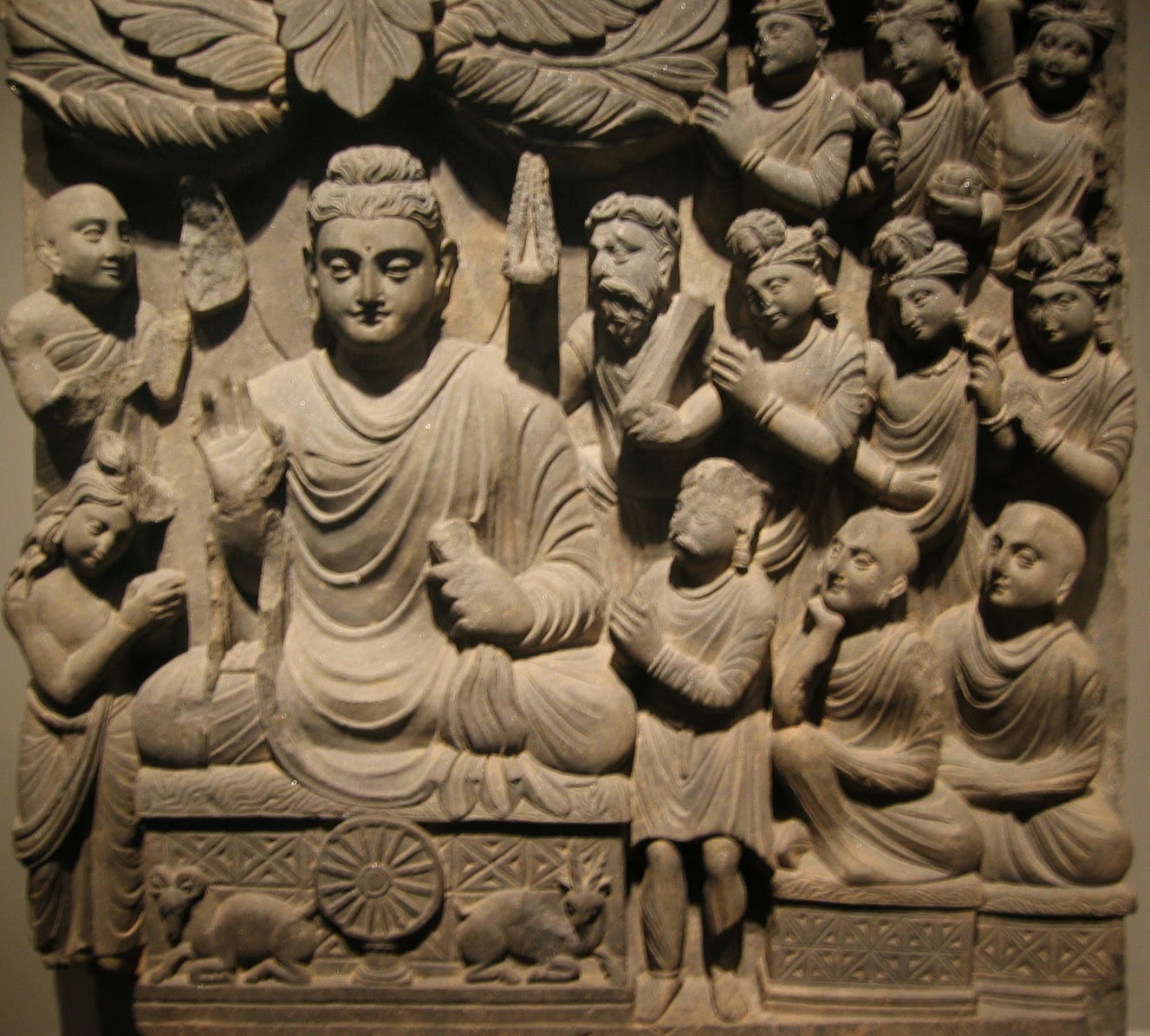
The Buddha History:
3. Belief in Nirvana :
4. Belief in Ahimsa :
Third Council:
Please Read Other Blogs...Must share with others!!!
1) Buddha: Its founder
2) Dhamma: His Teachings
3) Sangha: Order of buddhist monks and nuns.
The Buddha History:
- Also known as Sakyamuni or Tathagata.
- born in 563 BC on the Vaishakha Poornima Day at Lumbini (near Kapilavastu) in Nepal.
- His father Suddhodana was the Saka ruler.
- His mother ( Mahamaya of Kosala dynasty) died after 7 days of his birth. Brought up by stepmother Gautami.
- Married ad 16 to Yoshodhara. Enjoyed the married life for 13 years and had a son named Rahula.
- After seeing an old man, a sick man, a corpse and an ascetic, he decided to became a wanderer.
- Left his palace at 29( with Channa , the charioteer and his favorite horse, Kanthaka) in search of truth ( also called 'Mahabhinishkramana' or ' the Great renunciation) and wandered for 6 years.
- He first meditated with Alara Kalama, But he was not convinced that man could obtain liberation fron sorrow by mental discipline and knowledge. His next teacher was Udraka Ramputra. he then joined forces with five ascetcs- Kondana, Vappa, Bhadiya, Mahanama and Assagi, who were practicing the most rigorous self- mortification in the hope of wearing away their Karma and obtaining final bliss.
- For six years he tortured himself until he was nothing but a walking skeleton. But after six years, he felt that his fasts and penance had been useless. So he abandoned there things. the five disciples also left him.
- Attained 'Nirvana' or ' Enlightenment' at 35 at Gaya in Magadha ( Bihar) under the pipal tree.
- Delivered the first sermon at Sarnath where his five disciples had settled. His first sermon is called 'Dharmachakrapravartan' or 'Turning of the Wheel of Law'.
- Attained Mahaparinivarna at Kushinagar (identical with village kasia in Deoris district of Uttar Pradesh) in 483 BC at the age of 80 in the Malla Republic.
The Dhamma Indian History:
1. The Four Great Truths:
- The world is full of sorrow and misery.
- The cause of all pain and misery is desire.
- Pain and misery can be ended by killing or controlling desire.
- Desire can be controlled by following the Eight Fold Path.
2. The Eight Fold Path:
- It consist of Right Faith, Right Thought , Right Action, Right Livelihood, Right Efforts, Right Speech, Right Remembrance and Right Concentration.
3. Belief in Nirvana :
- When desire ceases, Rebirth ceases and nirvana is attained i.e. freedom from the cycle of birth, death and rebirth is gained by following the 8 fold path.
- According to Buddha, soul is a myth.
4. Belief in Ahimsa :
- One should not cause injury to any living being, animal or man.
5. Law of Karma :
- Man reaps the fruits of his past deeds.
The Sangha History :
- Consists of monks(Bhikshus or Shramanas) and nuns.
- Bhikshus acted as a torch bearer of the dhamma.
- Apart from Sangha, the worshippers were called Upasakas.
Buddhists Council :
The Monks gathered 4 times after the death of Buddha and the effect of these events had their effect on Buddhism.
First Council:
At Rajgriha, in 483 BC under the chairman ship of Mehakassaapa (King was Ajatshatru). Diveded the teachings of Buddha into two Pitakas- Vihaya Pitaka and Sutta Pitaka. Upali recited the Vinaya Pitaka and Ananda recited the Sutta Pitaka.
Second Council:
At Vaishali, in 383 BC under Sabakami (King was Kalasoka) . Followers diveided into Sthavirmadins and Mahasanghikas.
Third Council:
At Pataliputra, in 250 BC under Mogaliputta Tissa (King was Ashoka). In This , the third part of the Tripitaka was coded in the Pali language.
Fourth Council:
At kashmir (Kundalvan), in 72 AD under Vasumitra (King was kanishka). Vice Chairmanwas Ashwaghosha. Divided Buddhism into mahayana and Hinayana sects.
Important : In Mahayana, idol worship is there. It become popular in China, Japan, Korea, Afghanistan, Turkey and other Se countries.
Hinayana become popular in Magadha and srilanka. It believed in Individual salvation and not in idol worship. Apart from these two, there is a third vechile, called ' Vajrayana', which appeared in 8th century and grew rapidly in Bihar and Bengal. They did not treat meat, fish, wine etc, as a taboo in dietary habit and freely consumed them.
Buddhism Literature :
In pali language.
Buddhist scriptures in pali are commonly reffered to as Tripitakas, i.e. "Threefold Basket".
- Vinaya Pitaka: rules of disciplines in Buddhist monasteries.
- Sutta Pitaka: Largest, contains collection of Buddha's sermons.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka: Explanation of the philosophical principles of the Buddhist religion.
Please Read Other Blogs...Must share with others!!!




Comments
Post a Comment